|
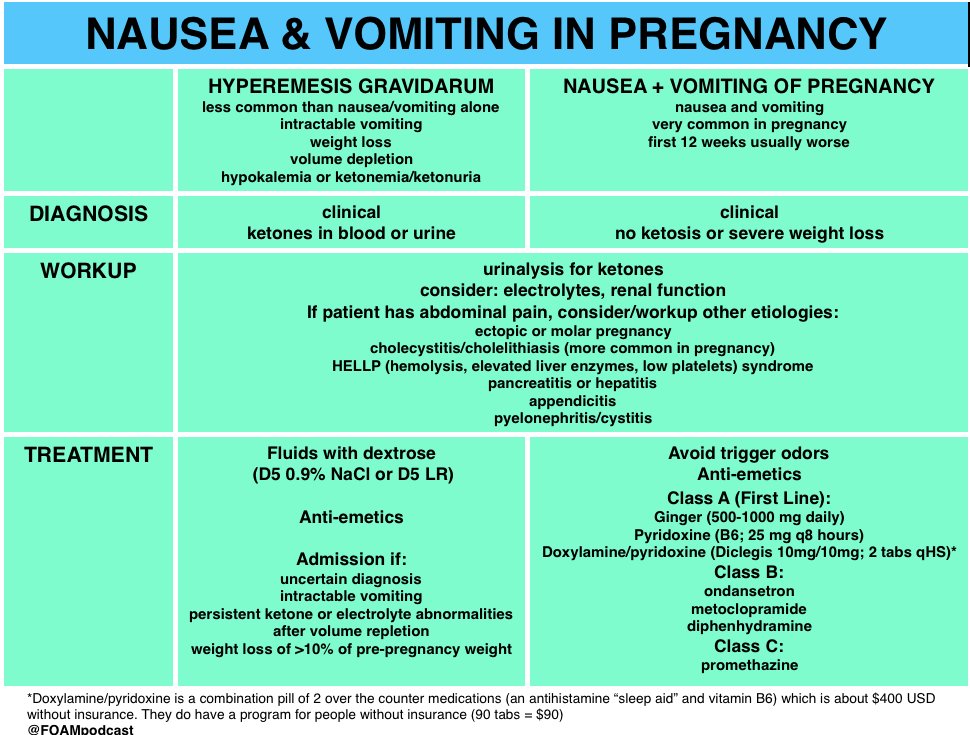
Hyperemesis gravidarum is characterized by persistent nausea and vomiting associated with ketosis and weight loss (>5% of prepregnancy weight). Hyperemesis gravidarum may cause volume depletion, electrolytes and acid-base imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, and even death. Severe hyperemesis requiring hospital admission occurs in 0.3-2% of pregnancies.
The only FDA-approved drug for treating nausea and vomiting in pregnancy is doxylamine/pyridoxine. However, antihistamines, antiemetics of the phenothiazine class, and promotility agents (eg, metoclopramide) have also been used to manage nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. In cases refractory to standard therapy, ondansetron and steroids may be considered.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |

Author
|
Proudly powered by Weebly