|
Pitfalls of pulse oximetry
In this lecture, we will discuss the pitfalls of using pulse oximeter in assessing patients with dyspnea. Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method of measuring the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in arterial blood. It has become a ubiquitous tool in clinical practice, providing a continuous estimate of a patient's oxygenation status. However, there are several important limitations and potential pitfalls associated with the use of pulse oximetry, particularly in the assessment of patients presenting with dyspnea or respiratory distress. The fundamental principle behind pulse oximetry involves the different absorption spectra of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin for red and infrared light. The ratio of these absorption values is used to calculate the oxygen saturation (SpO2). This calculation assumes that only two species of hemoglobin are present: oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin. However, in certain clinical situations, other hemoglobin species may be present, leading to inaccurate SpO2 readings. One such situation is carbon monoxide poisoning. Carboxyhemoglobin, formed by the binding of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin, has a similar absorption spectrum to oxyhemoglobin. Since oximeters misinterpret carboxyhemoglobin as 100% oxyhemoglobin, SpO2 will trend toward 100% in patients with significant carbon monoxide poisoning, potentially masking the severity of their condition. This can lead to a false sense of reassurance and delayed treatment. Another limitation of pulse oximetry is its inability to detect hypoxemia in the setting of abnormal hemoglobin species, such as methemoglobin and sulfhemoglobin. Methemoglobinemia can occur due to certain drugs, toxins, or inherited disorders, while sulfhemoglobinemia is typically associated with sulfur compound exposure. Sulfhemoglobinemia can mimic methemoglobinemia clinically and by SpO2 measurements. Since oximeters misinterpret methemoglobinemia as 85% oxyhemoglobin, SpO2 will trend toward 85% in patients with significant methemoglobinemia. Thus, SpO2 can either overestimate or underestimate the oxygen saturation of patients with methemoglobinemia or sulfhemoglobinemia. Furthermore, pulse oximetry does not consider hemoglobin level, and has limitations in accurately measuring oxygen saturation at extremes of hemoglobin concentration. For non-hypoxic cases of severe anemia with hemoglobin levels below 5 g/dL, pulse oximeters may overestimate the oxygen saturation. Conversely, in patients with polycythemia or high hemoglobin levels, pulse oximeters may underestimate the oxygen saturation. It is also important to note that pulse oximetry measures the functional saturation of hemoglobin, which may not accurately reflect the overall oxygen content of the blood, particularly in cases of dyshemoglobinemias or shifts in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve. Pulse oximetry does not consider A-a gradient, supplemental O2 can mask severe pulmonary process. In such situations, arterial blood gas analysis provides a more comprehensive assessment of oxygenation status and acid-base balance. Fluctuations in PaO2 can lead to rapid, unpredictable changes in SpO2 that may be missed by intermittent monitoring, thus, continuous SpO2 monitoring is suggested for dyspneic patients. In addition to these limitations, pulse oximetry can be affected by factors such as poor perfusion, motion artifacts, and the presence of certain dyes or pigments. Conditions such as hypothermia, hypotension, or peripheral vascular disease can lead to reduced peripheral perfusion, resulting in unreliable SpO2 readings. Similarly, excessive patient movement can introduce motion artifacts, compromising the accuracy of the measurements. Another pitfall is that pulse oximetry measures peripheral oxygen saturation, which can lag behind changes in central arterial oxygenation. This delay may mask acute deterioration in some patients. When assessing patients with dyspnea or respiratory distress, it is crucial to interpret pulse oximetry readings in the context of the patient's clinical presentation, physical examination findings, and other diagnostic modalities. Relying solely on pulse oximetry can potentially lead to missed diagnoses or inappropriate management decisions. Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) provides a more comprehensive assessment of oxygenation and acid-base balance. ABG allows the calculation of A-a gradient which helps clinicians narrow down the differential diagnosis for hypoxemia. One should consider ABG analysis when appropriate. In summary, while pulse oximetry is a valuable tool in clinical practice, healthcare professionals must be aware of its limitations, particularly in the assessment of patients with dyspnea or respiratory distress. Potential pitfalls include interference from abnormal hemoglobin species, inaccuracies at extremes of hemoglobin concentration, the inability to detect hypoxemia in certain conditions, and the effects of poor perfusion or motion artifacts. Integrating pulse oximetry findings with a comprehensive clinical evaluation, including arterial blood gas analysis when appropriate, is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of respiratory disorders. Take Home Message
0 Comments
Back pain Emergencies
Aortic syndrome or retroperitoneal bleeding
Spinal epidural abscess (SEA)
Cauda equina syndrome
Straight Leg Raise Test (SLRT)
The slump test
Spinal Metastases
Spinal Fractures
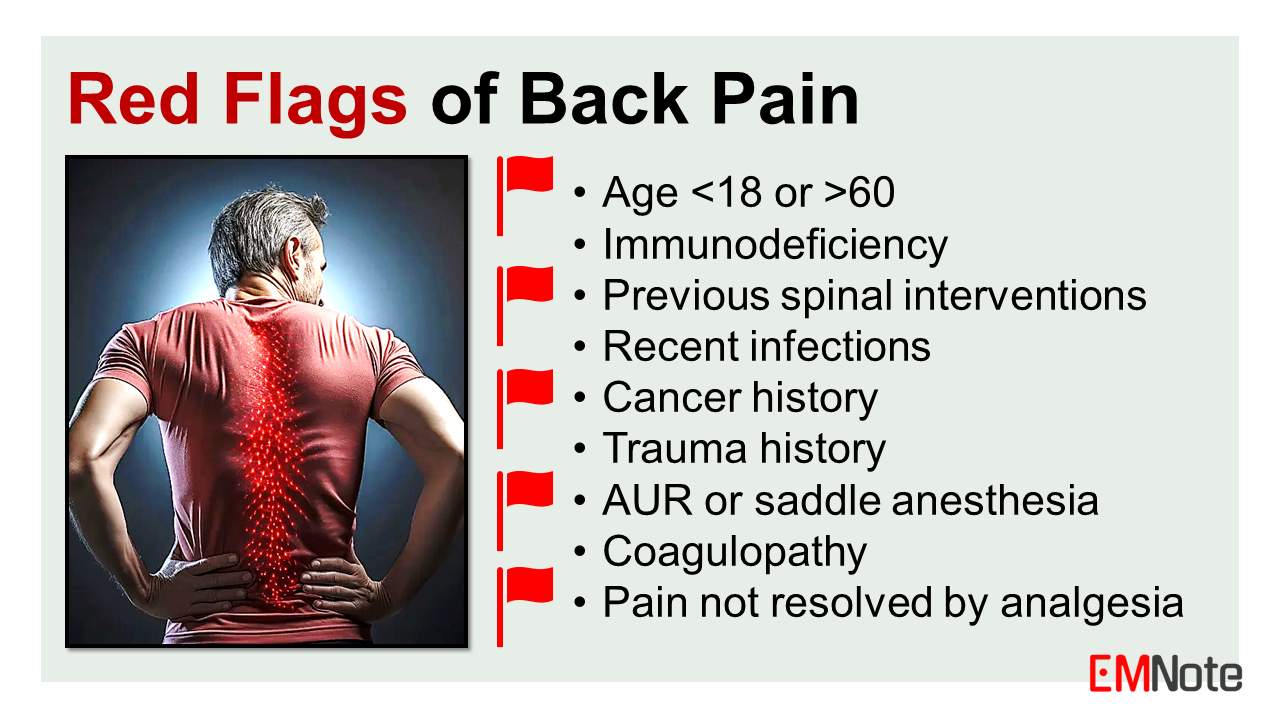
Red Flags for Back Pain
Important Physical Findings of patients with back pain
Diagnostic Tests for Back Pain
Management of Back Pain Emergencies
Take Home Message
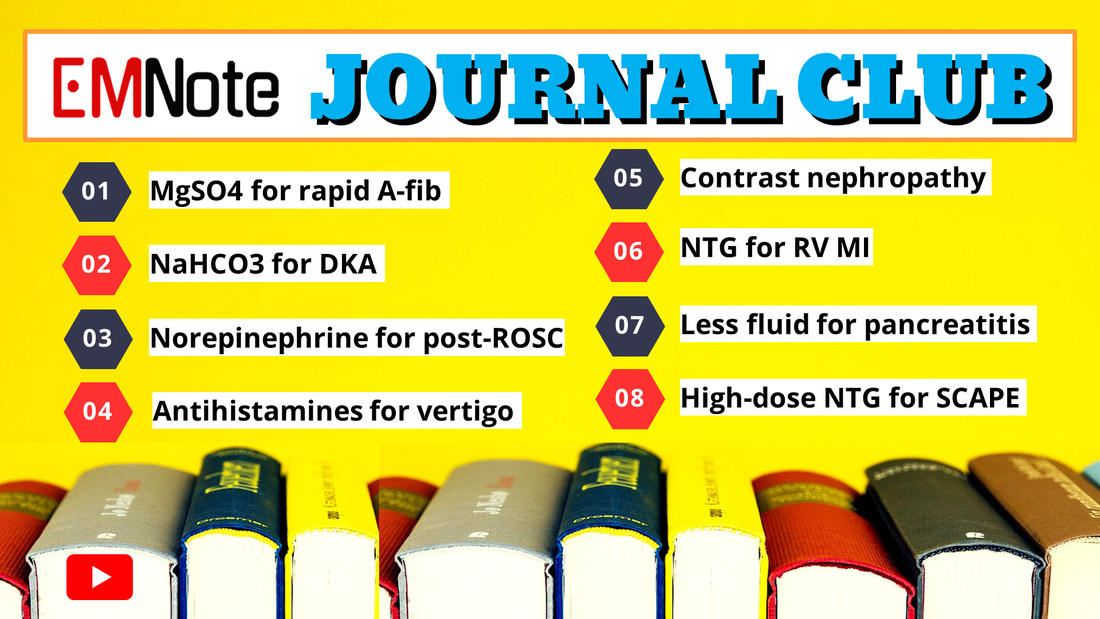
EM Literature #1
- MgS04 for rapid A-fib - NaHC03 for DKA - Norepinephrine for post-ROSC - Antihistamines for vertigo - Contrast nephropathy - NTG for RV MI - Less fluid for pancreatitis - High-dose NTG for SCAPE Venous Blood Gas as a Replacement for Arterial Blood Gas in Emergency Settings
Comparison between VBG and ABG
Benefits and Advantages of VBG
Clinical Applications of VBG
Limitations of VBG
Take Home Message
ACLS and BLS Lecture Notes:
In this video, we will delve into the protocols for responding to cardiac arrest, both non-shockable and shockable rhythms, as well as symptomatic bradycardia. By following the American Heart Association's algorithms, you will gain a clear understanding of the essential steps to take in these critical situations.
In conclusion, Immediate recognition and intervention are crucial in cardiac arrest or symptomatic bradycardia. The sooner treatment is administered, the higher the chances of positive outcomes. By following these ACLS guidelines, you will be well-equipped to confidently respond to cardiac emergencies and improve patient outcomes. |

Author
|
Proudly powered by Weebly